3. High-Performance Computing (HPC)
3.1. Overview of High-Performance Computing (HPC): architecture & components
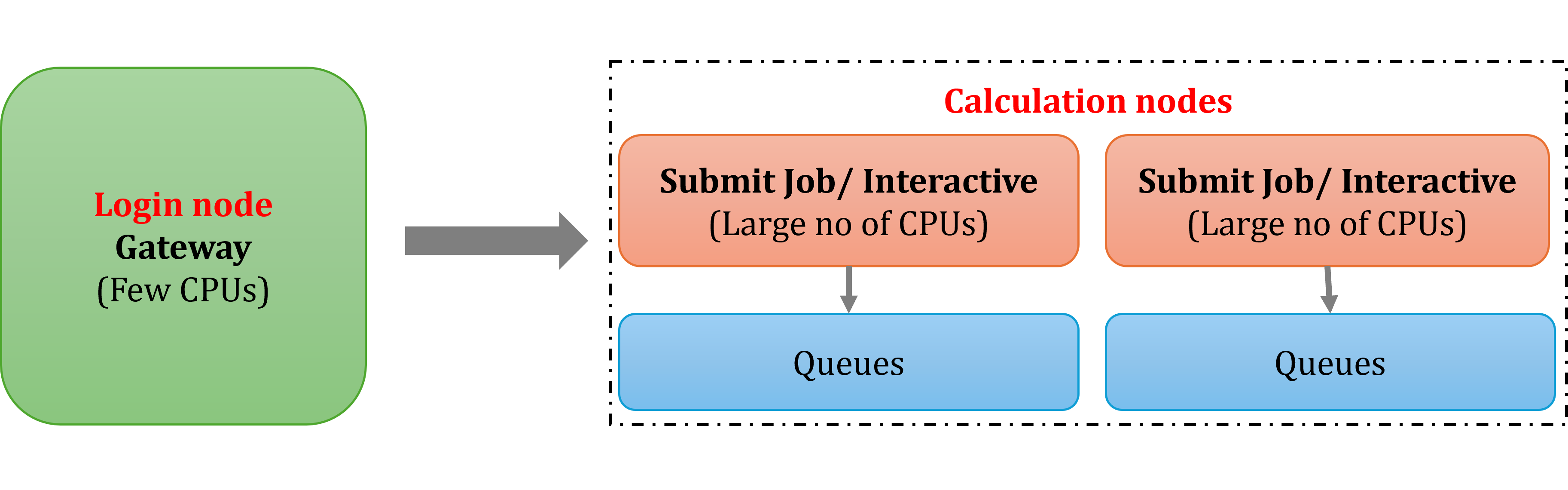
High-Performance Computing (HPC) systems consist of interconnected nodes forming clusters. Its usually a linux based server for managing nodes (i.e. CPUs) to perform large computations.
Note: Please click here for details related to H-Lab Server
Key components include:
- Login node: The login node is gateway to HPC cluster & calculation nodes. It has small memory and not designed for large calculation and analysis.
- Calculation node: The calculation node have large memory with multi-core processors or GPUs, used to perfom all the analysis. It can be used directly or with PBS command for submitting the job to the calculation node for performing analysis in the background.
- Storage Systems: Hierarchical storage includes high-speed scratch space and permanent home directories.
- Networking: High-speed interconnects (e.g., InfiniBand) enabling fast data transfer between nodes.
- Scheduler/Resource Manager: Software (e.g., PBS, SLURM) managing job submissions and resource allocation.
3.2. Connecting to HPC clusters
Accessing HPC systems typically involves:
- SSH (Secure Shell): Command-line access using
ssh user@hostname. - VPN/Two-Factor Authentication: Sometimes required for secure access.
- File Transfer Tools:
scp,rsync, or GUI-based tools such aswinscpfor moving files between local and remote systems.
scp: copies files between hosts on a network
(see below for command syntex)
scp [-346ABCOpqRrTv] [-c cipher] [-D sftp_server_path] [-F ssh_config] [-i identity_file] [-J destination] [-l limit] [-o ssh_option] [-P port] [-S program] source ... target
Note: info scp will shows all the details realted to scp including options.
rsync: a fast, versatile, remote (and local) file-copying tool
(see below for command syntex)
Local:
rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [DEST]
Access via remote shell:
Pull:
rsync [OPTION...] [USER@]HOST:SRC... [DEST]
Push:
rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [USER@]HOST:DEST
Access via rsync daemon:
Pull:
rsync [OPTION...] [USER@]HOST::SRC... [DEST]
rsync [OPTION...] rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/SRC... [DEST]
Push:
rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [USER@]HOST::DEST
rsync [OPTION...] SRC... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/DEST)
Note: for more details use info rsync.
3.3. Common directories
- Home Directory: Persistent storage, limited space, suitable for scripts and small files.
- Scratch Directory: High-speed, temporary storage for running computations; not backed up.
- Project Directories: Shared spaces for collaborative research, often with quotas.
- Archival Storage: Long-term, slower storage for completed projects or backups.
3.4. Best practices for using HPC
- Efficient Resource Usage: Request appropriate resources (CPUs, memory, runtime) for jobs.
- File Management: Regularly clean up scratch space and archive completed projects.
- Job Monitoring: Use tools (qstat, squeue, etc.) to track job status.
- Parallelization: Utilize parallel computing techniques to enhance performance.
- Documentation: Maintain scripts and workflows with comments and version control. (useful for others to use it in future)
References
- rsync. (n.d.). Retrieved March 25, 2025, from https://rsync.samba.org